Processors by year of release. Intel vs AMD processors: analysis and comparison of models
- 1. A little history
- 2. Pricing policy
- 3. Overclocking options
- 4. Processor for computer games
- 5. Final instructions
Every computer, no matter how it is used, is made up of identical basic components. The main element in any PC is the processor, which performs all computing operations, and the performance of this small part determines the performance of the system as a whole. Only two companies are fighting for leadership in the processor market, which we will talk about today and try to answer the age-old question - AMD or Intel, which is better?
A little history
Both companies began their journey in an era when computers occupied entire rooms, and the concept of a personal computer was just beginning to come into fashion. The first in this field was Intel, created in 1968 and becoming practically the only developer and manufacturer of processes. The brand's initial products were integrated circuits, but pretty soon the manufacturer focused only on processors. AMD was founded in 1969 and was initially aimed at the process market.

At that time, AMD processors became a product that appeared through active cooperation between two manufacturers. Intel's technical department supported the young competitor in every possible way and shared technologies and patents. After the company firmly found its feet, the manufacturers' paths diverged in different directions, and today the two global manufacturers collide with each other in every generation of processors.
Price policy
There are many solutions on the market, both from one manufacturer and from another. Taking the side of one company and completely abandoning the other is not so easy, because when choosing a processor you need to take into account many factors. To begin with, it is worth noting that both companies produce processors for all applications and for any budget:
- Office. Such processors have minimal technical characteristics and low cost, are designed to run office applications and are not designed for programs with high computing needs.
- Homemade. This type of process is usually more powerful than the office version, since it provides a performance reserve for casual gaming, but the cost of such an element is much higher.
- Gaming or professional. Computer games place certain demands on CPU power, and such a processor will cost a pretty penny.
If you are selecting a processor for work, then AMD offers inexpensive options for “stones” with good technical performance. The budget line from the manufacturer is characterized by low cost, excellent performance and reasonable energy consumption. However, Intel products, according to all experts, have a much higher power reserve. Thus, an AMD processor is excellent for a budget computer, but for work in resource-intensive applications, gaming and stable system operation in general, it is better to opt for Intel.
 Overclocking options
Overclocking options
Overclocking is a fairly popular way to increase the performance of a computer without the need to purchase additional hardware. However, for full overclocking, the processor must have a certain architecture and meet specific requirements.
If an Intel processor is better for gaming, then it is recommended to purchase an AMD processor for overclocking. Unlike its competitor, AMD has created processors that can operate at different clock speeds, which provides ample overclocking options. At the same time, you can overclock any processor from the line, but Intel allows you to experiment only with some models with the K index in the name. Other processors simply do not support overclocking and cannot change the clock speed. 
For those who plan to overclock a PC platform, it is better to purchase AMD, which operates stably at any frequency. At the same time, this effect is supported by both expensive eight-core processors and budget options.
Processor for computer games
Fans of clear graphics definitely choose Intel Core i5 and i7. The latest models from this manufacturer have shown high performance in the most “heavy” games and do an excellent job of visualizing any picture. Such processors belong to the gaming category.
However, AMD is not giving up its position so easily. Not long ago, a solution appeared that is perfect for a budget gaming computer - six-core Ryzen 5 chipsets. The result is an inexpensive and quite productive working platform. Although the verdict still adheres to Intel products, which are recognized as the best solution for a gaming computer.
One of the main factors when choosing a processor for gaming is its energy efficiency. Traditionally, Intel processors are better optimized both in terms of power consumption and operating temperatures. Therefore, if you do not want your computer to “heat like a stove,” it is better to join the blue camp, or save on the processor and take AMD, but additionally buy a powerful cooling system.
Final instructions
In 2019, both companies will introduce a new generation of processors that will have more advanced characteristics. At the moment, the best choice for a home computer in terms of price/quality ratio are two processors - Intel Core i5 and AMD Ryzen 5 1600.
Both stones have approximately the same parameters, but there are several very obvious differences:
- Both stones have the same number of cores, but in the case of AMD there is the notorious possibility of fairly simple overclocking. Therefore, it will be better suited for the future, and Intel will work more stable.
- Specific RAM format. An AMD processor reaches its full potential if it has a certain RAM frequency, which can create some difficulties. The Intel processor is much more interesting in this regard, because it does not create such strict restrictions.
- An Intel processor heats up much less, meaning you don’t have to spend additional money on organizing a cooling system. AMD gets quite hot and you will have to purchase a powerful cooler for it.
In any case, offers from all manufacturers have their own advantages and are tailored to fulfill specific tasks. If you are forced to stick to a strict budget, AMD offers an excellent line of inexpensive processors. In the case when you want to build a computer that can cope with any task, then Intel products have not yet been developed better for this purpose.
The question of which processor is better than AMD or Intel does not have a clear answer, because each component has a number of specific parameters and the choice of one or another option should be based on the purpose of the PC itself. An effective platform will demonstrate high performance only with the correct selection of all components that will enhance each other's performance.
Assembling a computer can be a very difficult task, especially if you are not experienced in such tasks. There are a huge number of components that you can use, but it is important to choose components that are compatible with each other and will provide maximum performance.
The central processing unit is one of the most important components of a computer; it is here that all calculations are performed. It controls the operation of all other components, so it is important to choose the right one. At the moment, devices from two manufacturers are available to you: AMD or Intel processor. These companies create almost all the PC processors in the world. But they are quite different from each other. In this article we will look at how these processors differ so that you can choose which processor is better amd or intel in 2016.
Before we move on to the detailed characteristics of the processor and technologies, let's go back to the roots and see how both companies started.
Intel appeared a little earlier than AMD, it was created by Robert Noyce and Gordon Moore in 1968. Initially, the company was developing integrated circuits, then began producing processors. The first processor was the Intel 8008 model. Back in the 90s, the company became the largest processor manufacturer. And he still continues to invent and implement new technologies.
Oddly enough, AMD or Advanced Micro Devices was created with the support of Intel. The company was created a year later - in 1969 and its goal was to develop microcircuits for computers. At first, Intel supported AMD, for example, by providing licenses for the use of technologies, as well as financially, but then their relationship soured and the companies became direct competitors. Now let's move closer to the processors themselves and their characteristics.
Price and performance
Both Intel and AMD offer processors in a wide price range. But AMD processors are cheaper. The cheapest are AMD Sempron and Athlon, these dual-core A-series processors sell starting at $30. The dual-core Intel Celeron G1820 is slightly more expensive at $45. But this does not mean that AMD chips are definitely better. Intel is known to give better performance for the same price. You'll get a more powerful processor if you choose a Celeron, Pentium, or Core from Intel. If you compare amd and intel 2016, the former consume less energy, generate less heat, and higher performance is confirmed by many tests.
But there are a few exceptions to this rule; AMD sells quad-core processors for much less than Intel, for example, you can get the A6-5400K for just $45. If you're running software that needs a lot of cores but can't afford an Intel Core i5, then you'll be better off with AMD. The same is true for eight-core AMD FX series processors, which are much cheaper than Intel Core i7.
AMD chips also provide the best integrated graphics cards. For example, the AMD A10-7870K allows you to play most games in low detail and up to 1080p resolution. Of course, this is not a gaming card, but it outperforms all Intel HD Graphics cards, so if you want to game on a budget device, then AMD is a better choice.
CPU overclocking

Most processors have a fixed clock speed and it is set at a level that ensures that the processor will operate as stable and for a long time as possible. Users who want to get more performance overclock the processor by increasing its frequency.
AMD supports overclocking much better than Intel. You can overclock both cheap processors for $45 and more expensive ones for $100. As for Intel, here you can overclock processors of only one category - Pentium, for $70. It is well suited for this task, and from a base frequency of 3.2 GHz it can be overclocked to 4.5 GHz. AMD FX series processors with a frequency of 5 GHz support overclocking up to 13 GHz, although this requires special cooling.
In fact, budget Intel processors are not designed for overclocking, but AMD ones are quite suitable. If you want to overclock, then AMD is a great choice. There are several high-end Intel chips, with eight or ten cores. They are much faster than AMD chips. But AMD has a lot of power headroom, so they dominate overclocking. You won't find anything faster for home use.
Gaming performance

Gaming is one of the most basic areas where a powerful processor is needed. AMD has several processors that come with an integrated ATI Radeon graphics card. They offer excellent value for money. Intel also has such solutions, but if you compare Intel and AMD processors, its performance is lower.
But there is one problem, AMD processors are not as fast as Intel, and if you compare AMD vs Intel, then Intel may perform better in heavy games. Intel Core i5 and i7 will perform much better in games if you use a good external graphics card. The difference between amd and intel processors is that Intel can produce 30-40 more frames per second.
Energy efficiency
The confrontation between AMD and Intel, or more precisely, AMD's attempts to keep up with Intel is much worse than it looks. Both companies are holding up well, but the processors need to consume a lot less power. Let's try to compare intel vs amd processors.
For example, the Intel Pentium G3258 consumes 53 Watts, and the A6-7400K from AMD consumes the same amount. However, in tests, Intel's chip is faster in many aspects, sometimes by a large margin. This means that the Intel chip will run faster while consuming less power, so the AMD will generate more heat and therefore produce more noise.
If the question is which processor is better amd or intel for a laptop, then energy efficiency is even more important because it directly affects battery life. Intel processors last longer, but Intel hasn't driven AMD out of the laptop market. AMD processors with integrated graphics are found on laptops over $500.
conclusions
AMD and Intel have been battling it out for two decades, but in the last few years Intel has started to gain the upper hand. New Pentium processors have slowly replaced AMD at various price points.
If you have the budget, then Intel is obviously the best solution. This will remain true if your budget allows you to purchase an Intel Core i5. AMD can't compete with Intel on performance, at least not yet.
If your budget is small, then perhaps you should look towards AMD, here the loss in performance is compensated by an increase in the number of cores. Such processors handle some operations faster, for example, AMD encodes video faster.
If we compare Intel and Amd 2016 processors, Intel is more energy efficient and therefore produces less heat and noise. For a regular computer, these features are not so important, but for a laptop, efficiency is very important.
But all is not lost with AMD; in 2017, the company is going to release a new architecture - Zen. Based on the available information, it is very promising. If you still want to buy AMD, then you should wait for the release of Zen.
Thus, the Intel processor is better than AMD, but in some situations the latter can give excellent performance and outperform Intel. For the Linux operating system, the manufacturer of the processor does not matter much. This is exactly the component that is fully supported by the kernel. Which processor to choose AMD or Intel in 2016, in your opinion? Which is better amd or intel? Which one would you choose? Write in the comments!
To complete the video from 16 bits ago about the history of Intel vs AMD:
Almost all modern technology cannot exist without a processor - the core of the electronic component. Despite the sufficient variety of modern manufacturers, the most popular are Intel processors, whose history goes back almost half a century.
The first CPUs appeared back in the 40s of the last century, but only in 1964, with the entry of IBM System/360 computing devices into the market, it was possible to claim the beginning of the computer era.
4-bit processors
In 1971, Intel introduced the first 4-bit processor, labeled 4004 and manufactured using 10 micron technology. The number of transistors in the chip was 2300, and the clock frequency was 740 kHz.
In 1974, an upgrade was made to the 4040 model. At the same time, the number of transistors increased to 3000 while maintaining the maximum clock frequency.
Both models were used by Nippon in the manufacture of calculators.
8-bit processors
They replaced 4-bit processors and were labeled 8008, 8080, 8085. Production began in 1972, and the last model appeared on the market in 1976. With the advent of these models, a noticeable increase in the processor clock frequency began from 500 kHz to 5 MHz. At the same time, the number of transistors increased from 3500 to 6500. 3, 6 and 10 micron technologies were used in production.
16-bit processors
The production of 16-bit processors began in 1978 and was initially considered as an intermediate stage before the development and launch of the 32-bit architecture, as it most fully meets modern requirements, especially since increasing competition required newer and more powerful processor models for electronics manufacturers .
The production of 16-bit processors began with the 8086 model, created using 3-micron technology and having a clock frequency of up to 10 MHz. The development of this type of processor ended in 1982 with the release of the 80286 model, which has a maximum clock frequency of 16 MHz. Among the features, we can note the possibility of using hardware protection for multitasking systems.
32-bit processors
The start of the development of 32-bit processors marked the beginning of the development and widespread introduction of computers. They served as the basis for the creation of personal computers, which are so widely used today. It is also worth noting that there are still quite a large number of working computers running 32-bit architecture processors.
The 32-bit architecture includes several lines and microarchitectures:
- He-x86 processors
- lines 80386 and 80486
- architecture and microarchitecture of Pentium, Celeron and Xeon
- NetBurst microarchitecture
In 1981, the iAPX 432 was first introduced as the first 32-bit He-x86 processor from Intel. It had an operating frequency of up to 8 MHz. Further developments in this line include the i860 and i960 processors, released in 1988-89. The same line included the XScale series of processors, presented to customers in 2000. XScale processors are widely used in the production of handheld computers.
Lines 80386 and 80486 were introduced in 1985 and 1989, respectively. Most often they were designated as 386 and 486 processors. Clock frequencies started at 20 MHz, and 1 micron technology was used in production.
The Pentium was first introduced in 1993 and was a processor with a clock frequency of 75 MHz, manufactured using a 0.6 micron process. Production of all Pentiums, as well as simpler Celeron models, continued until 2006. The latest model in the presented line is the Pentium Dual-Core, manufactured using 65nm technology and with a clock frequency of 1.86 GHz.
The NetBurst microarchitecture was first introduced in 2000 with the Pentium 4 model with a clock frequency of 1.3 MHz. As a result of further modernization, the frequency rose to 3.6 GHz, and the technological process used from 0.18 to 0.13 microns.
64-bit processors
Includes several microarchitectures:
- NetBurst
- IntelCore
- Intel Atom
- Nehalem
- Sandy Bridge
- Ivy Bridge
- Haswell
- Broadwell
- Skylake
- Kaby Lake
The production of 64-bit processors at Intel began in 2004, and in 2005 the Pentium 4D was released, intended for widespread use. During its production, a 90nm process was used, and the frequency was 2.66 GHz. Further developments include the 955 EE and 965 EE at 3.46 and 3.73 GHz.
IntelCore includes processors manufactured using the 65nm process technology. First introduced in 2006, they have frequencies from 1.86 GHz to 3.33 GHz with different cache sizes and bus frequencies.
The IntelAtom series has been produced since 2008 and is made using a 45nm process technology. It has a frequency from 800 MHz to 2.13 GHz. Quite simple and cheap processors used in the production of netbooks.
The Nehalem series was introduced to buyers in 2010. The series processors have clock speeds from 1.07 GHz to 3.6 GHz and include processors with 2, 4 and 6 cores.
SandyBridge and IvyBridge have been available since 2011 and include models from 1-core to 15-core with frequencies from 1.6 GHz to 3.6 GHz.
Haswell, Broadwell, Skylake and Kaby Lake include models with 2, 4 and 6 cores with frequencies from 3 GHz to 4.4 GHz.
Let's figure out what the main differences are between the processors of the world leaders - Intel and AMD.
We will also consider their positive and negative sides.
Major CPU Manufacturers
Everyone understands perfectly well that there are two leading companies in the computing market that are engaged in the development and production of the Central Processing Unit (central processing unit), or, more simply put, processors.

These devices combine millions of transistors and other logic elements, and are electronic devices of the highest complexity.
The whole world uses computers whose heart is an electronic chip from either Intel or AMD, so it’s no secret that both of these companies are constantly fighting for leadership in this area.
But let's leave these companies alone and move on to the average user, who is faced with a choice dilemma - what is preferable - Intel or AMD?
Whatever you say, there is not and cannot be a definite answer to this question, since both manufacturers have enormous potential, and their CPUs are capable of meeting the current requirements.
When choosing a processor for your device, the user primarily focuses on its performance and cost - relying on these two criteria as the main ones.
The majority of users have long been divided into two opposing camps, becoming ardent supporters of Intel or AMD products.
Let's look at all the strengths and weaknesses of the devices of these leading companies, so that when choosing a particular one, we rely not on speculation, but on specific facts and characteristics.
Advantages and disadvantages of Intel processors

So, what are the advantages of Intel processors?
- First of all, this is very high performance and speed in applications and games, which are most optimized for Intel processors.
- Under the control of these processors, the system operates with maximum stability.
- It is worth noting that the second and third level memory of Intel CPUs operates at higher speeds than in similar processors from AMD.
- Multithreading, which is implemented by Intel in CPUs such as Core i7, plays a big role in performance when working with optimized applications.
Advantages and disadvantages of AMD processors

- The advantages of AMD processors include, first of all, their affordability in terms of cost, which is perfectly combined with performance.
- A huge advantage is the multi-platform, which allows you to replace one processor model with another without the need to change the motherboard.
- That is, a processor designed for socket AM3 can be installed on socket AM2+ without any negative consequences.
- One cannot fail to note multitasking, which many AMD processors cope well with, simultaneously running three applications.
- In addition, FX series processors have quite good overclocking potential, which is sometimes extremely necessary.
- The disadvantages of AMD CPUs include higher power consumption than that of Intel, as well as operation of the second and third level cache memory at lower speeds.
- It should also be noted that most processors belonging to the FX line require additional cooling, which will have to be purchased separately.
- And another disadvantage is that fewer games and applications are adapted and written for the AMD processor than for Intel.
Current connectors from Intel

Today, many leading manufacturers of central processors are equipped with two current connectors. From Intel they are as follows:
- LGA 2011 v3 is a combined connector that is aimed at quickly assembling a high-performance personal computer for both servers and the end user. The key feature of such a platform is the presence of a RAM controller that successfully operates in multi-channel mode. Thanks to this important feature, PCs with such processors are characterized by unprecedented performance. It must be said that within the framework of such a platform an integrated subsystem is not used. Unlocking the potential of such chips is only possible with the help of discrete graphics. To do this, you should use only the best video cards;
- Thanks to LGA, you can easily organize not only a high-performance computing system, but also a budget PC. For example, a socket LGA 1151 It is perfect for creating a mid-price computing station, while at the same time it will have a powerful integrated graphics core of the Intel Graphics series and support DDR4 memory.
Current AMD connectors
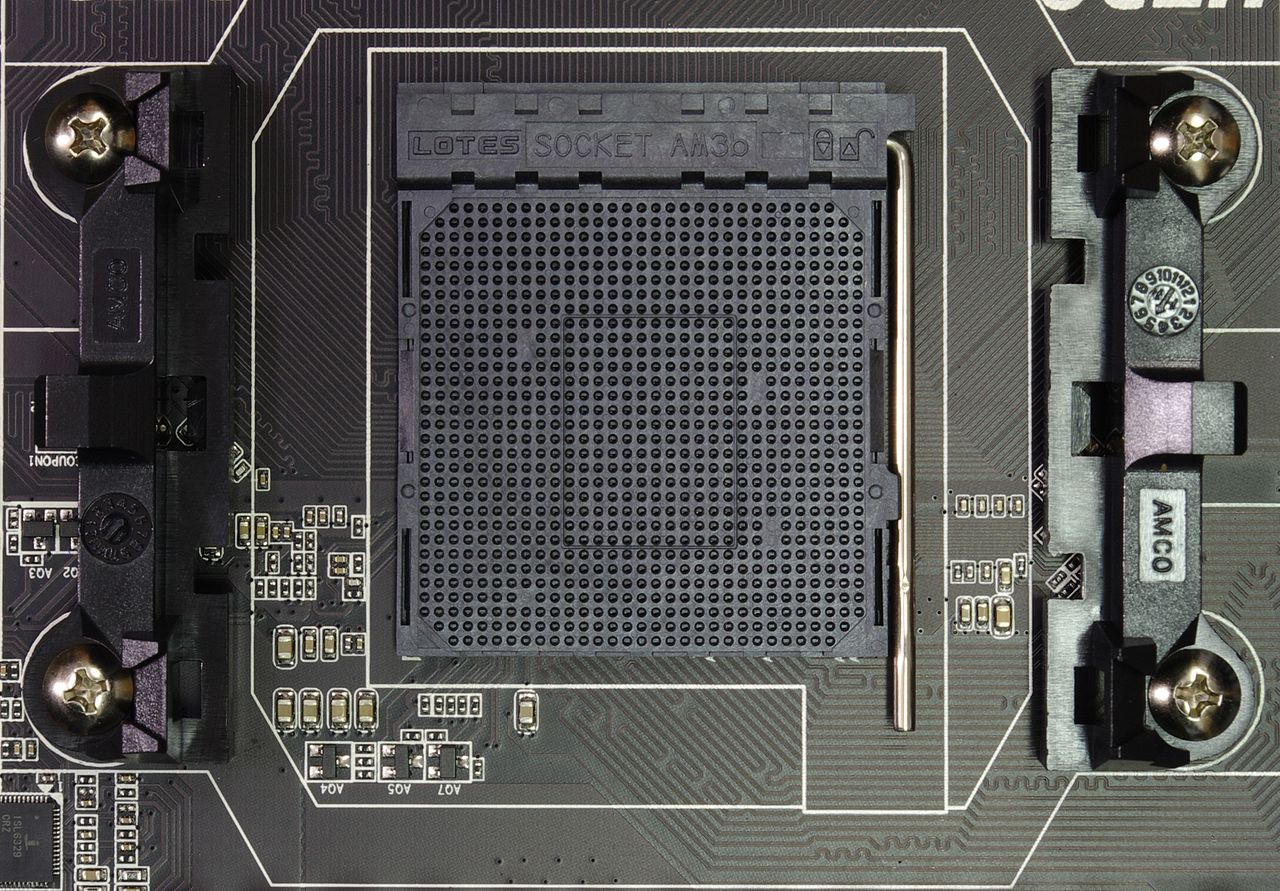
Today AMD is promoting the following processor sockets:
- The main computing platform for such a developer is considered AM3+. The most productive CPUs are considered to be the FX model range, which includes up to eight computing modules. In addition, such a platform supports an integrated graphics subsystem. However, here the graphics core is included in the motherboard, and is not integrated into the semiconductor crystals;
- the latest modern AMD processor socket – FM3+. AMD's new CPUs are intended to be used in desktop computers and media centers not only at entry-level, but also at mid-level. Thanks to this, the most modern integrated solution will be available to the average user for a fairly small amount.
Working possibilities

Many people first pay attention to the price of the processor. It is also important for them that he can easily solve the tasks assigned to him.
So, what can both organizations offer on this point? AMD is not known for outstanding achievements.
But this processor represents an excellent price-performance ratio. If you configure it correctly, you can expect stable operation without any complaints.
It is worth noting that AMD managed to implement multitasking. Thanks to such a processor, various applications can be easily launched.
With its help, you can simultaneously install the game and surf the vast expanses of the Internet.
But Intel is known for more modest results in this area, which is confirmed by the comparison of processors.
It would not be superfluous to pay attention to the availability of overclocking, during which the performance of an AMD processor can easily be increased by twenty percent compared to standard settings.
To do this, you just need to use additional software.
Intel beats AMD in almost everything except multitasking. In addition, Intel is working with
So you should select the motherboard and power supply much more carefully to prevent freezes due to insufficient power.
Power consumption chart for Intel and AMD It's the same story with heat dissipation. It is quite high in older models. As a result, a standard cooler has difficulty coping with increased cooling.
Therefore, when purchasing a CPU from AMD, you must additionally purchase high-quality cooling from any decent company. Don't forget that high-quality fans make much less noise.
Socket type and performance

We should also say something about performance. After AMD acquired ATI, its creators were able to successfully integrate most of the graphics processing capabilities into the processor cores. Such efforts have paid off successfully.
Those who use an AMD chip for gaming should have no doubt that they are getting good performance, which is much better than the performance of equivalent chips from Intel (this is especially true for those who use a card with ATI graphics).
If it comes to heavy multitasking, then it is better to choose Intel, since it has HyperTreasing technology.
However, this advantage can only be exploited when the software application is capable of multitasking, that is, the ability to divide tasks into several small parts.
If the user needs a gaming processor, it is better to combine an AMD processor with a video card.
So, there is a big difference between intel and amd processor sockets. When choosing the right option, consider the differences between them listed in this article. This will make choosing the right option much easier.
AMD processors first appeared on the market in 1974, following the presentation by Intel of its first 8080-type models and were their first clones. However, the very next year the am2900 model of its own design was introduced, which was a microprocessor kit that began to be produced not only by the company itself, but also by Motorola, Thomson, Semiconductor and others. It is worth noting that the Soviet microsimulator MT1804 was also made on the basis of this kit.
AMD Am29000 processors
The next generation - Am29000 - full-fledged processors that combine all the components of the kit into one device. They were a 32-bit processor based on the RISC architecture, with an 8 KB cache. Production began in 1987 and ended in 1995.
In addition to its own developments, AMD also produced processors manufactured under license from Intel and bearing similar markings. So, the Intel 8088 model corresponded to Am8088, Intel 80186 - Am80186, and so on. Some models were upgraded and received their own markings, slightly different from the original ones, for example Am186EM - an improved analogue of the Intel 80186.

AMD C8080A processors
In 1991, a line of processors designed for desktop computers was introduced. The series was designated Am386 and used microcode developed for the Intel 80386. For embedded systems, similar processor models were launched into production only in 1995.

AMD Am386 processors
But already in 1993, the Am486 series was introduced, intended for installation only in its own 168-pin PGA connector. The cache ranged from 8 to 16 KB in upgraded models. The family of embedded microprocessors is designated Elan.

AMD Am486DX processors
Series K
In 1996, production of the first family of the K series began, designated K5. To install the processor, a universal socket was used, called Socket 5. Some models of this family were designed for installation in Socket 7. The processors had a single core, the bus frequency was 50-66 MHz, and the clock frequency was 75-133 MHz. The cache was 8+16 KB.

AMD5k series processors
The next generation of the K series is the K6 processor family. During their production, proper names begin to be assigned to the kernels on which they are based. So, for the AMD K6 model the corresponding code name is Littlefood, AMD K6-2 - Chomper, K6-3 - Snarptooth. The standard for installation in the system was a Socket 7 and Super Socket 7 connector. The processors had one core and operated at frequencies from 66 to 100 MHz. The first level cache was 32 KB. For some models there was also a second level cache, 128 or 256 KB in size.

AMD K6 Processor Family
Since 1999, the production of Athlon models began, part of the K7 series, which have received widespread and well-deserved recognition from many users. In the same line there are also budget models Duron, as well as Sempron. The bus frequency ranged from 100 to 200 MHz. The processors themselves had clock frequencies from 500 to 2333 MHz. They had 64 KB of first level cache and 256 or 512 KB of second level cache. The installation connector was designated Socket A or Slot A. Production ended in 2005.

AMD K7 series
The K8 series was introduced in 2003 and includes both single-core and dual-core processors. The number of models is quite diverse, as processors have been released for both desktop computers and mobile platforms. Various connectors are used for installation, the most popular of which are Socket 754, S1, 939, AM2. The bus frequency ranges from 800 to 1000 MHz, and the processors themselves have clock speeds from 1400 MHz to 3200 MHz. L1 cache is 64 KB, L2 - from 256 KB to 1 MB. An example of successful use is some Toshiba laptop models based on Opteron processors, codenamed after the core codename - Santa Rosa.

AMD K10 Processor Family
In 2007, the release of a new generation of K10 processors began, represented by only three models - Phenom, Athlon X2 and Opteron. The processor bus frequency is 1000 - 2000 MHz, and the clock frequency can reach 2600 MHz. All processors have 2, 3 or 4 cores depending on the model, and the cache is 64 KB for the first level, 256-512 KB for the second level and 2 MB for the third level. Installation is carried out in connectors such as Socket AM2, AM2+, F.
The logical continuation of the K10 line is called K10.5, which includes processors with 2-6 cores, depending on the model. The processor bus frequency is 1800-2000 MHz, and the clock frequency is 2500-3700 MHz. The work uses 64+64 KB of L1 cache, 512 KB of L2 cache and 6 MB of third-level cache. Installation is carried out in Socket AM2+ and AM3.
AMD64
In addition to the series presented above, AMD produces processors based on the Bulldozer and Piledriver microarchitecture, manufactured using a 32 nm process technology and containing 4-6 cores, the clock speed of which can reach 4700 MHz.

AMD a10 processors
Nowadays, processor models designed for installation in the FM2 socket, including hybrid processors of the Trinity family, are very popular. This is due to the fact that the previous implementation of Socket FM1 did not receive the expected recognition due to relatively low performance, as well as limited support for the platform itself.
The core itself consists of three parts, including a graphics system with a Devastrator core, which came from Radeon video cards, a processor part from the x-86 Piledriver core and a north bridge, which is responsible for organizing work with RAM, supporting almost all modes, up to DDR3- 1866.
The most popular models of this family are A4-5300, A6-5400, A8-5500 and 5600, A10-5700 and 5800.
The flagship models of the A10 series operate with a clock frequency of 3 - 3.8 GHz, and when overclocked they can reach 4.2 GHz. The corresponding values for A8 are 3.6 GHz, with overclocking - 3.9 GHz, A6 - 3.6 GHz and 3.8 GHz, A4 - 3.4 and 3.6 GHz.
It might be useful to read:
- Creating polls in Telegram How to like in Telegram;
- Lead camera engineer for Sony Xperia on the development of mobile photography, Sony technologies and the future;
- How to transfer mobile game saves to another device?;
- How to fake correspondence on VKontakte and other social networks?;
- Controlling a computer without a mouse, under Windows XP;
- Fixing the error “BSvcProcessor has stopped working”;
- Completely remove Skype from your computer How to completely remove Skype from your computer;
- Convert PNG images to ICO How to make ico from jpeg;